
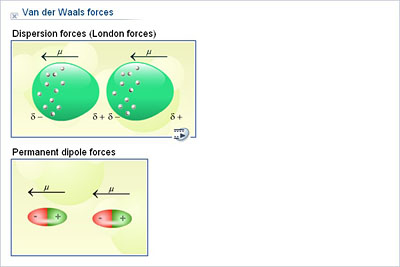

For this reason, transition metals can form two, three, or four coordinate covalent bonds with other atoms! Zinc, iron, and magnesium are examples of such metals that usually bond with enzymes inside our bodies. In this type of covalent bond, both electrons in the bond are donated by a single atom.ĭue to their unique orbital structure, transition metals can easily accept electrons from other atoms. A coordinate covalent bond, sometimes referred to as a dative bond, is a special subtype of covalent bond that often forms between transition metals. Recall that covalent bonds are simply bonds formed between atoms in which electrons are unevenly shared. For more information on this, be sure to refer to our guide on isomers. Molecules and chemical compounds can often be drawn in a variety of ways. This resonance form is highly unlikely to occur! In contrast, creating only single bonds in ozone would create formal charges of -1, -1, and +2, which are much higher formal charges. This is the relatively stable form of ozone, as the formal charges of each species are fairly low. One atom has a charge of 0, while the other two have charges of -1 and +1. In the ozone molecule, each oxygen atom has a different formal charge. Thus, it can be calculated using the following equation:įormal charge = # valence electrons - nonbonding electrons - bonding electrons ÷ 2 Formal charge refers to the amount of “functional” charge an atom would have, assuming all electrons are shared equally. The most stable resonance form is one that provides the lowest formal charge of the atoms. The resulting combined configuration may be shown with a dashed line. The electrons within the molecule are said to be delocalized and can be found with equal probability within any of these resonance structures. In general, the bonds within such a molecule are assumed to be a combination of all of these resonance structures. A molecule that displays resonance may have electrons in any of these resonance configurations at any given time. A resonance structure is an alternative model of covalent bonding. One advantage to using a Lewis dot diagram is that resonance structures can be shown. Be sure to understand these terms well, as they will be high-yield on Test Day! At the end of this guide, there are also several MCAT-style questions you can use to test your knowledge. Throughout this guide, there will be several important terms marked in bold. Some exist between individual atoms of a molecule, while others exist between molecules. There are a variety of bonds, or attractive forces, that exist.

Atomic bonds and intermolecular attractions are the foundation for many additional concepts in organic chemistry and biochemistry.Ĭhemical bonds are chemical interactions that create an attractive force between atoms or molecules. Understanding how atoms and molecules interact with each other is crucial for much of the chemistry section of the MCAT. What holds everything in the universe together? Why don’t atoms and molecules randomly split apart and float away? The answer lies in bonding and molecular interactions. Part 1: Introduction to bonds and interactions


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
